This content is from:APP亚博娱乐
Understanding Defensive Equity
An Institutional Investor Sponsored Statement
Defensive equities seek to provide a “best of both worlds”: delivering the equity risk premium to achieve wealth accumulation, but by investing in less-risky equity securities to promote wealth preservation.
要查看完整报告的PDF,请单击此处。
2016年7月1
介绍
Over a 40-year working life, defined contribution (DC) plan savers try to maximize two basic investment outcomes: wealth accumulation and wealth preservation. However, these objectives present a basic tradeoff: for many retirement savers, the investments designed to promote wealth accumulation (equities) are different from the investments designed to promote wealth preservation (e.g., cash, bonds). Defensive equities seek to provide a “best of both worlds”: delivering the equity risk premium to achieve wealth accumulation, but by investing in less-risky equity securities to promote wealth preservation.
防守优惠
在金融领域最古老的一个结论是,劳r-risk stocks deliver returns that are “too high” compared to what traditional models predict.2 As shown in Figure 1, over the long term, lower-risk U.S. stocks (left side) have delivered approximately the same average return as higher-risk stocks (right side). Defensive equity3.strategies seek to capture this premium by investing across a range of low-risk stocks, with the objective of achieving market-like returns but with less volatility.4.
是什么推动防守溢价?
Various theories seek to explain why defensive stocks perform as well as they do. One of the oldest and most tested is “leverage aversion,” which considers what happens to stock prices when a meaningful subset of investors are unable or unwilling to use leverage.

一般而言,具有激进返回目标的股权投资者有两种选择:1)投资更高风险的股票,希望获得高度回报,或2)使用杠杆放大较低风险股票的回报。然而,在杠杆厌恶世界中,投资者在选项1和2之间没有选择。相反,他们被迫参加选项1:投资更高风险的股票。
The resulting high demand for higher- risk stocks means their prices get bid up and their expected returns go down. The opposite holds for lower-risk, or defensive, stocks: Because there is less demand for them, their prices are bid lower and thus may be expected to perform better than they otherwise would.
是什么让股票“防御”?
There are many ways to evaluate whether a security is defensive. These fall into two categories: fundamental and quantitative. From a fundamental perspective, companies with low risk may have relatively high margins, sustainable earnings and low credit risk.5.从量化的角度来看,风险低的公司可能是具有较低β或对市场的敏感性的公司,或对市场的敏感性或低波动性。我们认为这两个类别对于识别防御性公司都很有用,并且该组合可能会产生更强大的真正防御性股票的投资组合。
防御和定义贡献
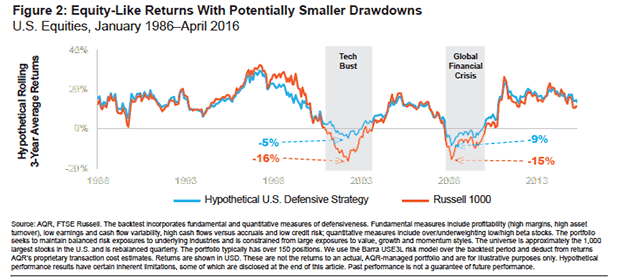
防御性股票可能是最适合满足财富积累和财富保护的双胞胎目标之一。Figure 2 charts the rolling threeyear average returns of two portfolios: a hypothetical U.S. large-cap defensive equity strategy and the Russell 1000. In good times the returns are comparable,which supports the idea that defensive equities may achieve returns on par with passive equities and thus provide a similar engine for growth.
但是,差异可以在图2的阴影区域中看到 - 当较低波动导致较小的拉长时,展示防御性股票可能更好地在降低市场的情况下更好。6.当投资者通过市场缩减时,投资者越来越多的时间,这种特点显然是近期退休。但它也可能有助于年轻的储蓄者,他们可能不太可能在严重和潜在的延长熊市后扔进毛巾,维护他们需要积累足够节省的退休金所需的分配。
1For more, see Frazzini, Friedman and Kim (2012), “Understanding Defensive Equity.”
2早期研究包括黑色(1972)。
3.防御性股权,低β,最低差异,低波动性 - 这些名称全部描述了一般寻求超重安全证券和体重风险证券(相对于资本化重量基准)的投资策略。
4.防御保费的证据是普遍存在的。Beyond the U.S., we find decades of evidence in international markets and in other asset classes—such as bonds and credit—that point to the same basic conclusion: Defensive strategies may generate returns similar to those of overall markets but with less volatility (and thus generally smaller drawdowns).
5.与前面的证据,安全,有利可图和稳定的公司历史上历史上赢得了较高的风险,不可稳健的公司,如Piotroski(2002),Novy-Marx(2012),Asness,Frazzini和Pedersen(2012年)所示。
6.Over the full period show in Figure 2, the average volatility and total return of the Russell 1000 are 15% and 11%, respectively. For the Hypothetical Defensive Strategy the average volatility and total return are 12% and 12%, respectively.
Bibliography
Asness,A.,Frazzini,A.,Pedersen,L.H.(2012),“质量减去垃圾”,工作纸。
黑色,F.(1972),“资本市场均衡与受限制借款”,营业杂志那Vol. 45, No. 3, pp. 444-455.
Frazzini,A.,弗里德曼,J.,Kim,H.(2012),“了解防御性股权”,AQR白皮书。
Novy-Marx,Robert(2013),“其他一面:毛利率溢价,”金融经济学杂志108(1), 2013, 1-28. Piotroski, Joseph D. (2000), “Value Investing: The Use of Historical Financial Statement Information to Separate Winners from Losers,”会计研究杂志,38,1-41。

AQR is a global investment management firm
雇用系统,研究驱动的
管理替代和传统的方法
strategies. As of June 30, 2016, we managed
约1590亿美元用于制度
投资者和投资专业人员。
披露
This material has been provided to you solely for information purposes and does not constitute an offer or solicitation of an offer or any advice or recommendation to purchase any securities or other financial instruments and may not be construed as such. The factual information set forth herein has been obtained or derived from sources believed by the author and AQR Capital Management, LLC (“AQR”) to be reliable but it is not necessarily all-inclusive and is not guaranteed as to its accuracy and is not to be regarded as a representation or warranty, express or implied, as to the information’s accuracy or completeness, nor should the attached information serve as the basis of any investment decision. The information set forth herein has been provided to you as secondary information and should not be the primary source for any investment or allocation decision.
过去的性能不是未来表现的保证。
多元化不会消除体验投资损失的风险。
Broad-based securities indices are unmanaged and are not subject to fees and expenses typically associated with managed accounts or investment funds. Investments cannot be made directly in an index. The Russell 1000 Index is a stock market index that represents the highest-ranking 1,000 stocks in the Russell 3000 Index, which represents about 90% of the total market capitalization of that index.
This document is not research and should not be treated as research. This document does not represent valuation judgments with respect to any financial instrument, issuer, security or sector that may be described or referenced herein and does not represent a formal or official view of AQR.
表达的观点反映了目前的目前的日期,作者和AQR都没有承诺向您建议您在此表达的意见中的任何变更。不应该假设作者或AQR将在未来进行投资建议,该建议与本文所表达的观点一致,或使用本文描述的任何或全部的技术或所有分析方法在管理客户账户中。这里包含的信息仅截至所示日期的当前信息,并且可以被后续的市场事件或其他原因取代。本文提供的图表和图表仅用于说明目的。本文中的任何内容构成了投资,法律,税收或其他建议,也没有依赖投资或其他决定。
无法保证投资策略将是成功的。历史市场趋势是实际未来市场行为的可靠指标或未来任何可能差异的特定投资的未来表现,可能不应依赖于此。
根据其特定的投资目标和财务状况,本文讨论的投资策略和主题可能不适合投资者。假设的性能结果(例如,定量逆端)具有许多固有的局限性,其中一些但不是全部在此描述。没有任何代表性,任何基金或账户都将或可能达到类似于本文所示的利润或损失。事实上,假设绩效结果和随后由任何特定交易计划实现的实际结果存在常见差异。假设性能结果的一个局限性之一是它们通常是由于后敏感而制备的。此外,假设交易不涉及财务风险,并且没有假设的交易记录可以完全占对实际交易中的金融风险的影响。例如,尽管有交易损失,承受损失或坚持特定贸易计划的能力是物质点,这可能会对实际交易结果产生不利影响。本文包含的假设绩效结果代表了当前在上面写的日期生效的定量模型的应用,并且不能保证模型将在未来保持不变,或者将来的目前模型的应用将产生类似的结果,因为在假设的绩效期间的相关市场和经济条件普遍存在,不一定会发生重现。通常有许多与市场有关的其他因素,或者执行任何特定的交易计划,这些贸易计划在编写假设绩效结果方面不能完全占,这一切都可能对实际交易结果产生不利影响。 Discounting factors may be applied to reduce suspected anomalies. This backtest’s return, for this period, may vary depending on the date it is run. Hypothetical performance results are presented for illustrative purposes only. In addition, our transaction cost assumptions utilized in backtests, where noted, are based on AQR’s historical realized transaction costs and market data. Certain of the assumptions have been made for modeling purposes and are unlikely to be realized. No representation or warranty is made as to the reasonableness of the assumptions made or that all assumptions used in achieving the returns have been stated or fully considered. Changes in the assumptions may have a material impact on the hypothetical returns presented.
